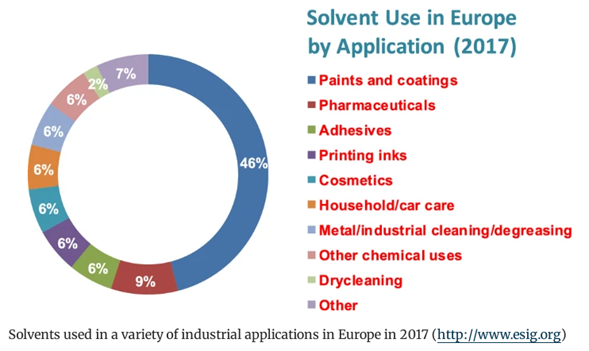
5 Main applications of ethyl lactate: green and eco-friendly solvent in coating and polyurethane industry
Ethyl lactate is one of the most important green solvents obtained from the processing of agricultural products such as corn. Due to its environmental and safety characteristics, this solvent is considered a suitable alternative to traditional petroleum solvents. Ethyl lactate is 100% biodegradable, non-corrosive, and non-cancerous, and has become popular in environmentally friendly industries. Due to its high boiling point, low vapor pressure, and good solubility strength, it is applied in the coating, paint, cosmetic products, and food industries. This solvent is also used as an effective cleaner in the polyurethane industry and in the removal of fats and oils. Replacing ethyl lactate with chlorinated and petroleum solvents reduces environmental impact and increases employee safety. Research has shown that improving ethyl lactate extraction processes increases industrial efficiency and maintains its environmentally friendly properties. For this reason, the use of ethyl lactate in the chemical industry and the production of green products is expanding and is being recognized as a new standard for sustainable solvents.
Physical and chemical properties of ethyl lactate
Ethyl lactate has a high boiling point, low vapor pressure, low surface tension and excellent solubility strength. These characteristics make it perform best in the coating, paint, and polyurethane industries. In addition, ethyl lactate, as a stable and safe biosolvent, enhances the quality of finished products and reduces environmental risks.
Application of Ethyl Lactate in the Coating and Paint Industry
به دلیل قدرت حلالی بالا، جایگزین مناسبی برای حلالهای نفتی مانند تولوئن، استون و زایلن در صنایع پوشش و رنگ شده است. استفاده از این حلال دوستدار محیط زیست باعث افزایش ایمنی محیط کار، کاهش آلودگی هوا و محافظت از سلامت کارکنان میشود. کیفیت نهایی رنگ و پوشش تولید شده با اتیل لاکتات یکنواختتر و مقاومتر است. به علاوه، این حلال باعث تسهیل در فرآیند تولید و افزایش بهرهوری خطوط تولید میشود.
Application of Ethyl Lactate in the Polyurethane Industry
In the polyurethane industry, ethyl lactate acts as an efficient and safe cleaner. Its high solubility makes it dissolve all kinds of polyurethane resins and remove greases, oils, adhesives, and solid fuels from the surface of metals. The use of this green solvent has replaced harmful chlorinated solvents and reduced the negative environmental impact. This property has made ethyl lactate a popular choice in workshops and industrial plants.
Environmental and Safety Benefits of Ethyl Lactate
In addition to industrial application, it has significant benefits for the environment and employee health. This solvent is non-cancerous, biodegradable and recyclable, reducing environmental and health risks. The use of ethyl lactate as an eco-friendly solvent helps reduce pollutants and consume non-renewable resources, and it is also economically viable. Also, this solvent reduces the need for heavy-duty protective equipment and higher safety in industrial environments.
New Opportunities and Applications of Ethyl Lactate
The market for green solvents is growing, and ethyl lactate has investment opportunities and new application development due to its unique properties. Innovation in product development, the development of new applications, and strategic collaborations with key stakeholders can lead to a competitive advantage. Paying attention to environmental regulations and maintaining the health of employees increases the use of ethyl lactate in various industries. In addition to the coating and polyurethane industries, new research shows that ethyl lactate can also have effective applications in the printing, adhesives, and industrial cleaners industries.
Useful Links and Resources
- List of Green Sweeteners on the website
- Scientific Reference on Ethyl Lactate
- Wikipedia: Ethyl Lactate
Text References: Doble, M., & Kruthiventi, A. K. (2007). Alternate solvents. Green chemistry and engineering, 93-104
Image References: Winterton, N. (2021). The green solvent: A critical perspective. Clean technologies and environmental policy, 23(9), 2499-2522.